Interpersonal Relation Development
INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIP DEVELPMENT
INTRODUCTION
Interpersonal relationships are the cornerstone of human interaction, shaping our experiences, emotions, and overall well-being. From familial bonds to friendships, romantic partnerships, and professional connections, relationships permeate every aspect of our lives. Understanding the dynamics of interpersonal relationship development is crucial in the realm of behavioral science, as it offers insights into the complexities of human social interactions and provides strategies for fostering healthy, fulfilling connections.
Interpersonal relationships serve as the fabric of human society, intricately weaving together the threads of connection, understanding, and mutual support. From the bonds we form with family members to the friendships we cultivate and the professional alliances we forge, relationships shape our experiences, influence our emotions, and profoundly impact our lives.
Understanding the intricacies of interpersonal relationship development is not only essential for personal growth and well-being but also holds significant relevance in the realm of behavioral science, where the study of human social dynamics unveils the complexities of our interactions and offers invaluable insights into fostering healthy, fulfilling connections.
IMPORTANCE
Importance of Interpersonal Relationships:
- Social Support: Interpersonal relationships provide a vital source of social support, offering comfort, encouragement, and assistance during times of need. Whether facing challenges or celebrating successes, having a network of supportive relationships contributes to emotional resilience and well-being.
- Emotional Regulation: Relationships play a significant role in emotional regulation, influencing how individuals express, interpret, and manage their emotions. Close relationships provide a safe space for emotional expression, validation, and empathy, helping individuals navigate the complexities of their inner world.
- Identity Formation: Interpersonal relationships contribute to identity formation by shaping how individuals perceive themselves and others. Through interactions with family members, friends, and peers, individuals develop a sense of self-concept, self-esteem, and social identity, influencing their beliefs, values, and behaviors.
- Health and Well-being: Research has consistently shown that strong social connections are linked to better physical and mental health outcomes. Engaging in meaningful relationships reduces the risk of stress-related illnesses, depression, and anxiety, while also promoting longevity and overall well-being.
PROCESS OF INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIP DEVELPOMENT
Process involves:-
- Initiation: The first stage of interpersonal relationship development involves initiating contact and establishing rapport with others. This may involve initial encounters, introductions, or exchanges that set the foundation for future interaction.
- Exploration: During the exploration stage, individuals engage in reciprocal exchanges to learn more about each other's interests, values, and personalities. This phase often involves self-disclosure, active listening, and the exchange of information to deepen understanding and connection.
- Intensification: As relationships progress, the intensification stage is marked by increased closeness, intimacy, and commitment. Individuals may experience heightened emotional connection, trust, and reliance on each other, leading to deeper bonds and mutual investment in the relationship.
- Stabilization: In the stabilization stage, relationships reach a more stable and predictable state, characterized by established routines, norms, and patterns of interaction. Couples or groups may develop shared rituals, traditions, and symbols that reinforce their sense of unity and cohesion.
- Maintenance: Maintaining healthy relationships requires ongoing effort and communication to address challenges, resolve conflicts, and meet each other's needs. This stage involves nurturing trust, respect, and reciprocity while adapting to changing circumstances and evolving dynamics.
- Termination: Not all relationships last indefinitely, and the termination stage involves the dissolution of relationships through either natural attrition or deliberate choice. This phase may be marked by grief, sadness, or relief, depending on the circumstances surrounding the end of the relationship.
- Miscommunication: Misunderstandings and misinterpretations of verbal and nonverbal communication can lead to conflicts. Differences in communication styles, language barriers, and ambiguous messages may contribute to misunderstandings between individuals.
- Differences in Values and Beliefs: Disagreements over values, beliefs, and priorities can lead to conflicts in interpersonal relationships. When individuals hold contrasting views on important issues such as religion, politics, morality, or lifestyle choices, it can create tension and discord within the relationship.
- Expectations: Conflicts may arise when individuals have different expectations about roles, responsibilities, or behavior within the relationship. When expectations are not clearly communicated or aligned, it can lead to disappointment, frustration, and conflict.
- Lack of Trust: Conflicts may arise from a lack of trust between individuals within the relationship. Trust issues can stem from past betrayals, dishonesty, or breaches of confidence, leading to suspicion, insecurity, and conflict.
- Varying Interests: Differences in interests, hobbies, and preferences between individuals can contribute to conflicts in relationships. When partners or friends have divergent interests or spend significant time pursuing separate activities, it can create feelings of neglect, boredom, or disconnect, leading to conflict.
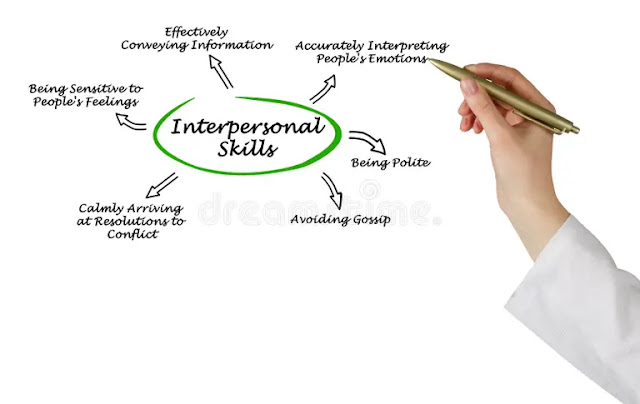
WAYS TO IMPROVE INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIP DEVELOPMENT
Improving interpersonal relationship development involves a combination of self-awareness, communication skills, empathy, and effort.
Here are several ways to enhance interpersonal relationships:
- Active Listening: Practice active listening by focusing on the speaker, maintaining eye contact, and paraphrasing their message to demonstrate understanding. Avoid interrupting and offer supportive gestures to show you're engaged in the conversation.
- Empathy: Put yourself in the other person's shoes to understand their perspective, emotions, and experiences. Show empathy by acknowledging their feelings and validating their experiences, even if you don't necessarily agree with them.
- Communication Skills: Enhance your communication skills by expressing yourself clearly, honestly, and respectfully. Use "I" statements to convey your thoughts and feelings without blaming or accusing others. Be open to feedback and willing to address misunderstandings promptly.
- Conflict Resolution: Develop effective conflict resolution skills to navigate disagreements and resolve conflicts constructively. Focus on finding mutually beneficial solutions, rather than engaging in win-lose dynamics. Practice active listening, compromise, and negotiation to reach a resolution that respects everyone's needs and interests.
- Conflict Resolution: Learn to navigate conflicts and disagreements in a healthy and constructive manner. Practice active listening, empathy, and compromise to find mutually acceptable solutions. Avoid blame, criticism, or defensiveness, and focus on resolving issues collaboratively.
- Seek Support: Don't hesitate to seek support from trusted friends, family members, or professionals when facing challenges in your relationships. Counseling, therapy, or support groups can provide valuable guidance, perspective, and tools for strengthening interpersonal connections.
CONCLUSION
In essence, interpersonal relationship development is a dynamic and multifaceted process that shapes our social connections, emotional experiences, and overall quality of life. By recognizing the significance of relationships and understanding the stages of relationship development, individuals can cultivate healthier, more fulfilling connections and navigate the complexities of human interaction with greater insight, empathy, and resilience. In the realm of behavioral science, the study of interpersonal relationships offers invaluable insights into human behavior, social dynamics, and strategies for fostering positive relationship outcomes, ultimately enriching our understanding of what it means to be human.
-By Nandini Goyal






Comments
Post a Comment